Discover effective strategies for preventing and treating acne with our comprehensive guide. Learn about the causes of acne, different types of acne, and proven treatment options. With expert tips on prevention and home remedies, our website offers a reliable source of information for those looking to achieve clear and healthy skin.
Say Goodbye to Acne: Proven Strategies for Clearing Up Your Skin
I. Definition of Acne
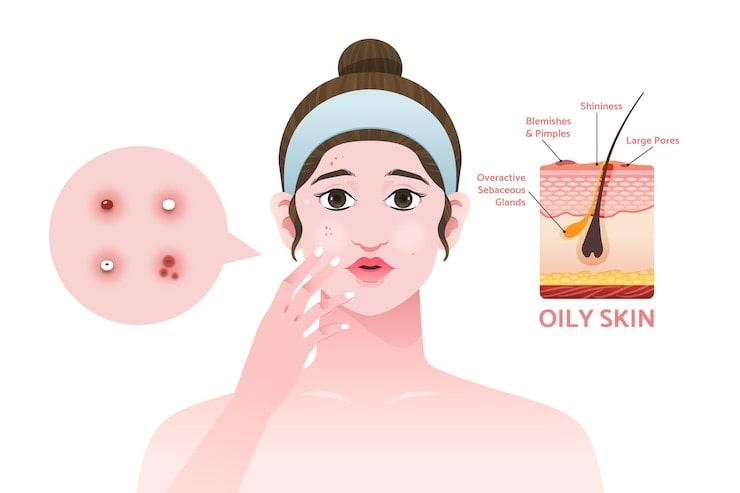
Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to the formation of pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads. Acne can occur at any age, but it's most common during puberty and adolescence.

definition-of-acne
Addressing acne is important for several reasons. First, acne can cause emotional distress and negatively impact self-esteem. Second, severe acne can lead to permanent scarring. Finally, acne can be a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as hormonal imbalances or polycystic ovary syndrome.
In this article, we'll provide a clear overview of acne, including its causes, types, and effective treatments. We'll also offer expert tips on preventing and managing acne, as well as home remedies that can help soothe and heal the skin. With our reliable and up-to-date information, you'll be equipped to take control of your acne and achieve clear, healthy skin.
II. Causes of Acne
Acne can have a variety of causes, and understanding these causes is key to effectively managing the condition. Here are some of the most common causes of acne:

acne-causes-reasons
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes, particularly during puberty, can lead to an increase in sebum production. Sebum is an oily substance produced by the sebaceous glands that can clog pores and lead to the development of acne. Hormonal changes can also occur during menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, which can trigger acne breakouts.
Genetics
Acne can be inherited from parents, and those with a family history of acne are more likely to develop the condition. This is because genetics can influence sebum production, skin inflammation, and the development of bacteria on the skin.
Diet
While diet is not a direct cause of acne, certain foods can trigger inflammation in the body, which can lead to the development of acne. Foods high in sugar and carbohydrates, such as white bread and pasta, can cause blood sugar spikes that lead to inflammation. Additionally, dairy products and high-glycemic foods have also been linked to acne breakouts.
Stress
Stress can trigger the release of hormones such as cortisol, which can increase sebum production and lead to the development of acne. Stress can also cause inflammation in the body, which can exacerbate existing acne.
By understanding the causes of acne, you can take steps to manage the condition and prevent breakouts. In the next section, we'll explore the different types of acne and how they can be treated.
III. Types of Acne
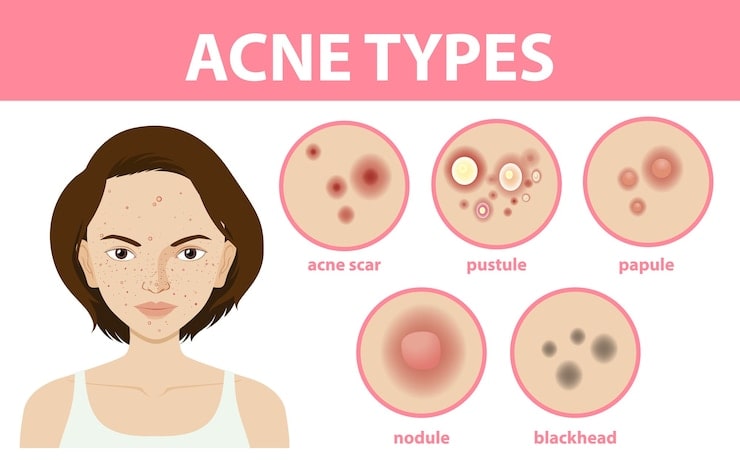
Acne can present in several different forms, each with its own characteristics and treatment options. Here are some of the most common types of acne:
Types Of Acne
Blackheads
Blackheads, also known as open comedones, occur when pores become clogged with oil and dead skin cells. The clog is open to the air, which causes it to darken and appear as a black spot on the skin.
Whiteheads
Whiteheads, also known as closed comedones, are similar to blackheads but have a closed surface. They are formed when a pore becomes clogged with oil and dead skin cells, but the clog does not open to the air.
Papules
Papules are small, red, and raised bumps on the skin that occur when hair follicles become inflamed. They can be tender to the touch and often occur in clusters.
Nodules
Nodules are large, painful, and deep-seated lumps that form under the skin. They are often caused by a buildup of bacteria and can take weeks or even months to heal.
Cysts
Cysts are similar to nodules but are larger and filled with pus. They are often painful and can leave scars if not treated promptly.
By understanding the different types of acne, you can better identify your own symptoms and seek appropriate treatment. In the next section, we'll explore some of the most effective treatments for acne, including both over-the-counter and prescription options.
IV. Treatment for Acne

Treatment For Acne
There are several effective treatments available for acne, and the right approach will depend on the severity of your symptoms and your skin type. Here are some of the most common treatments for acne:
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are applied directly to the skin and can be purchased over-the-counter or prescribed by a dermatologist. They work by reducing oil production, unclogging pores, and reducing inflammation. Some common topical treatments include:
Benzoyl Peroxide:Benzoyl peroxide works by killing bacteria on the skin that can cause acne. It also helps to reduce oil production and unclog pores. It can be found in many over-the-counter acne products.
Salicylic Acid:Salicylic acid works by exfoliating the skin and unclogging pores. It is often found in cleansers, toners, and spot treatments.
Retinoids:Retinoids are derived from vitamin A and work by reducing inflammation and unclogging pores. They can be prescribed by a dermatologist and are available in both topical and oral forms.
Oral Medications
Oral medications are often used to treat moderate to severe acne and are prescribed by a dermatologist. They work by reducing inflammation and killing bacteria on the skin. Some common oral medications include:
Antibiotics: Antibiotics work by killing bacteria on the skin that can cause acne. They are often prescribed in combination with topical treatments.
Isotretinoin: Isotretinoin is a powerful medication used to treat severe acne that has not responded to other treatments. It works by reducing oil production and unclogging pores. However, it has significant side effects and must be closely monitored by a dermatologist.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels work by removing the top layer of skin, which can help to unclog pores and reduce inflammation. They can be performed by a dermatologist or aesthetician and may require multiple treatments.
Light Therapy
Light therapy, also known as phototherapy, uses specific wavelengths of light to kill bacteria on the skin and reduce inflammation. It can be performed by a dermatologist and may require multiple treatments.
By understanding the different treatment options for acne, you can work with your dermatologist to develop a customized treatment plan that is right for you. In the next section, we'll explore some natural remedies and lifestyle changes that can help to prevent and manage acne.
V. Prevention of Acne
While acne is a common skin condition that affects many people, there are several steps you can take to prevent breakouts from occurring. Here are some ways to prevent acne:

Prevention Of Acne
Keeping Skin Clean
Keeping your skin clean is important to prevent acne. Be sure to wash your face twice a day with a gentle cleanser and warm water. Avoid scrubbing your skin too hard or using hot water, as this can irritate your skin and make acne worse.
Avoiding Harsh Products
Avoid using harsh products on your skin, such as exfoliants or scrubs. These can irritate your skin and make acne worse. Instead, look for gentle products that are designed for acne-prone skin.
Using Non-Comedogenic Products
Non-comedogenic products are designed not to clog pores. Look for products that are labeled non-comedogenic, such as makeup, sunscreen, and moisturizer.
Eating a Healthy Diet
Eating a healthy diet can help to prevent acne. Avoid eating foods that are high in sugar, such as candy and soda, and instead, opt for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Managing Stress
Stress can trigger acne breakouts, so it's important to manage stress levels. Try stress-relieving activities, such as yoga, meditation, or exercise.
By following these steps, you can help to prevent acne breakouts and maintain healthy, clear skin. However, if you do experience acne, there are several effective treatments available. In the next section, we'll explore some natural remedies for acne that you can try at home.
VI. Home Remedies for Acne
Acne is a common skin condition that can be frustrating to deal with, but there are several home remedies that can help reduce the appearance of acne and prevent future breakouts. Here are some effective home remedies for acne:

Home Remedies For Acne
Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is a natural essential oil that has antibacterial properties, making it an effective treatment for acne. Dilute a few drops of tea tree oil with a carrier oil, such as coconut oil, and apply it to the affected area with a cotton swab. Leave it on for 15-20 minutes before rinsing it off with warm water.
Honey and Cinnamon
Honey and cinnamon have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, making them effective for treating acne. Mix a tablespoon of honey with a teaspoon of cinnamon powder to form a paste. Apply the paste to the affected area and leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing it off with warm water.
Vera
Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties, making it an effective treatment for acne. Apply aloe vera gel directly to the affected area and leave it on for 15-20 minutes before rinsing it off with warm water.
Green Tea
Green tea contains antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties, making it an effective treatment for acne. Brew a cup of green tea and allow it to cool. Apply the cooled tea to the affected area with a cotton ball and leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing it off with warm water.
In summary, home remedies for acne can be effective in reducing the appearance of acne and preventing future breakouts. Tea tree oil, honey and cinnamon, aloe vera, and green tea are all natural remedies that can help improve the appearance of acne-prone skin. However, it's important to remember that home remedies may not work for everyone and to consult with a dermatologist for severe or persistent acne.
VII. When to See a Dermatologist
Acne is a common skin condition that can usually be managed with over-the-counter treatments, such as topical creams and cleansers. However, in some cases, acne can be severe or persist despite using these treatments. Here are some signs that it's time to see a dermatologist for your acne:

When To See A Dermatologist
Severe Acne
If your acne is severe and covers a large portion of your face or body, it may be time to see a dermatologist. Severe acne can be painful and may lead to scarring if left untreated.
Acne that Doesn't Respond to Over-the-Counter Treatments
If you've been using over-the-counter treatments for several weeks and haven't seen any improvement in your acne, it may be time to see a dermatologist. A dermatologist can prescribe stronger medications, such as topical or oral antibiotics, to help clear up your acne.
Acne that Leaves Scars
If your acne is leaving scars on your skin, it's important to see a dermatologist as soon as possible. Scarring can be difficult to treat and may be permanent if left untreated.
In summary, if you have severe acne, acne that doesn't respond to over-the-counter treatments, or acne that leaves scars, it's important to see a dermatologist. A dermatologist can provide personalized treatment options and help prevent long-term damage to your skin.
VIII. Conclusion
Acne is a common skin condition that affects people of all ages. While it's usually not a serious medical condition, it can be frustrating and cause significant self-esteem issues. In this article, we've discussed the causes, types, treatments, prevention, home remedies, and when to see a dermatologist for acne.
To summarize, acne is caused by a combination of factors such as hormonal changes, genetics, diet, and stress. There are several types of acne, including blackheads, whiteheads, papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts. Treatment options include topical treatments, oral medications, chemical peels, and light therapy. Prevention strategies include keeping skin clean, avoiding harsh products, using non-comedogenic products, eating a healthy diet, and managing stress. Home remedies such as tea tree oil, honey and cinnamon, aloe vera, and green tea may also be helpful for mild cases of acne.
It's important to seek treatment for acne, especially if it's severe, persistent, or causing scarring. Seeing a dermatologist can provide personalized treatment options and help prevent long-term damage to your skin.
In conclusion, if you're struggling with acne, don't hesitate to speak with a dermatologist. They can help you manage your symptoms and achieve clearer, healthier skin.
References:
[1] American Academy of Dermatology. (n.d.). Acne.
https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/acne-and-rosacea/acne
[2] Mayo Clinic. (2021, January 21). Acne.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/acne/symptoms-causes/syc-20368047






